
Strategies agreed to minimize the risk to each patient must be recorded before commencement of surgery. The risk of WLCS must be noted specifically in the preoperative team brief and WHO time out.All surgeons who undertake pelvic procedures on patients maintained in the Lloyd-Davies/lithotomy positions should be aware of well leg compartment syndrome (WLCS).ConclusionĪll surgeons who carry out abdominopelvic surgical procedures should be aware of well leg compartment syndrome, and instigate policies within their own institution to reduce the risk of this potentially life-changing complication. Key recommendations for the adoption of perioperative strategies to facilitate prevention and effective treatment of well leg compartment syndrome are presented. These guidelines encompass the risk factors (both patient- and procedure-related), diagnosis and management of the condition. A systematic analysis of the available peer-reviewed literature was undertaken to provide an evidence base from which these guidelines were developed. These guidelines represent the collaboration of a multidisciplinary group of colorectal, vascular and orthopaedic surgeons, acting on behalf of their specialty associations in the UK and Ireland. This condition may have devastating consequences for postoperative recovery, including loss of life or limb, and irreversible disability.
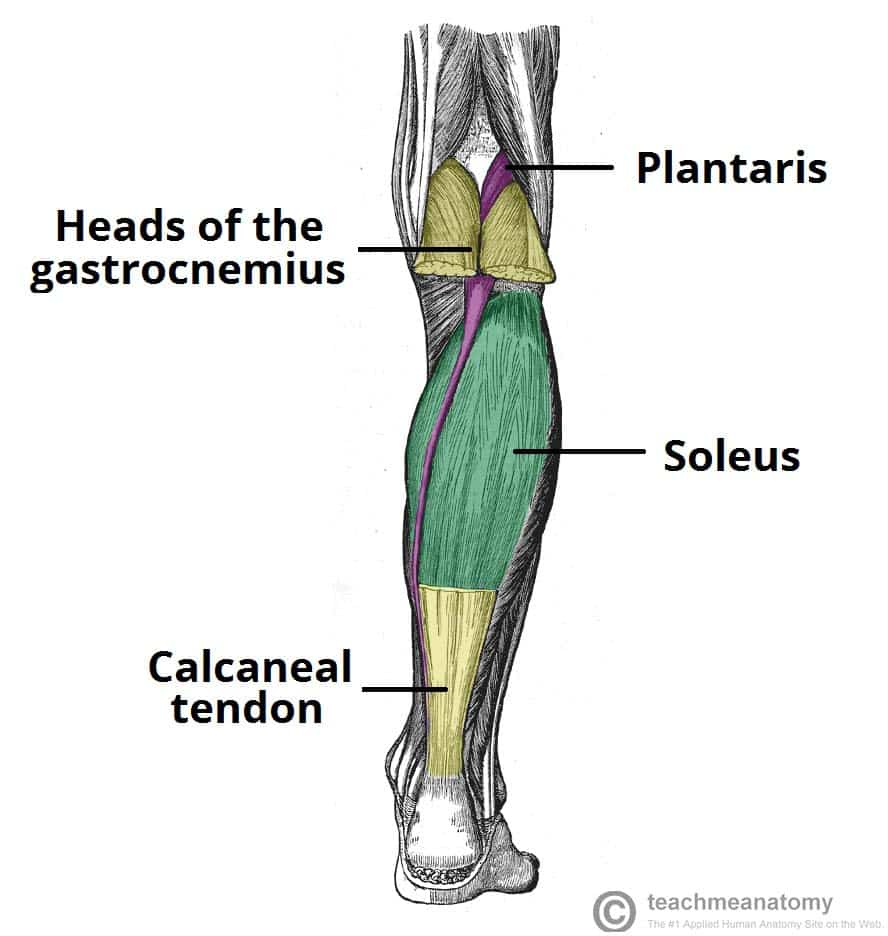
Patients undergoing prolonged pelvic surgery may develop compartment syndrome of one or both lower limbs in the absence of direct trauma or pre-existing vascular disease (well leg compartment syndrome).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
